Oracle PL/SQL Records Type with Examples
What is Record Type?
A Record type is a complex data type which allows the programmer to create a new data type with the desired column structure.
- It groups one or more column to form a new data type
- These columns will have its own name and data type
- A Record type can accept the data
- As a single record that consists of many columns OR
- It can accept the value for one particular column of a record
- Record type simply means a new data type. Once the record type is created, it will be stored as a new data type in the database and the same shall be used to declare a variable in programs.
- It will use the keyword 'TYPE' to instruct the compiler that it is creating the new data type.
- It can be created at "database level" which can be stored as database objects, used all-over the database or it can be created at the "subprogram levels", which is visible only inside the subprograms.
- The database level record type can also be declared for the table columns so that single column can hold the complex data.
- The data in these data type can be accessed by referring to their variable_name followed by period operator (.) followed by column_name i.e. '<record_type_variable_name>.<column_name>'
Syntax for declaration at the database level:
CREATE TYPE <type_name_db> IS RECORD ( <column 1> <datatype>, );
In the first syntax, we can see the keyword 'CREATE TYPE' this instructs the compiler to create the record type named "type_name_db" with the specified column as a database object.
This is given as an individual statement and not inside any block.
Syntax for declaration at subprogram level:
DECLARE TYPE <type_name> IS RECORD ( <columnl> <datatype>, ); BEGIN <execution_section>; END;
In the syntax, we are creating the record type named "type_name" only inside the subprogram.
In both declaration method, the way of defining the column and data type is similar.
Example 1: RECORD Type as Database Object
In this program, we are going to see how to create "Record type" as a database object. We are going to create record type 'emp_det' with four columns. The columns and their data type are as follows:
- EMP_NO (NUMBER)
- EMP_NAME (VARCHAR2 (150))
- MANAGER (NUMBER)
- SALARY (NUMBER)
CREATE TYPE emp_det IS RECORD ( EMP_NO NUMBER, EMP_NAME VARCHAR2(150), MANAGER NUMBER, SALARY NUMBER ); /Output:
Type created
Code Explanation:
- The above code will create type emp_det as a database object.
- It will have 4 column emp_no, emp_name, manager and salary as defined.
- Now 'emp_det' is a similar to other data type (like NUMBER, VARCHAR@, etc.) And it is visible in the entire database. Hence this can be used in the entire database to declare the variable of this type.
Output:
Created the type 'emp_det' as record type at the database level.
Example 2: Record Type at Subprogram level- Column level access
In this example, we are going to see how to create a record type at subprogram level and how to populate and fetch the values from it by column level.
We are going to create 'emp_det' record_type at subprogram level, and we are going to use the same to populate and to display data from it.
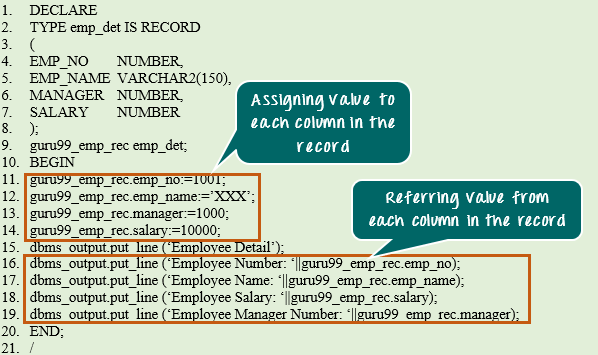
DECLARE
TYPE emp_det IS RECORD
(
EMP_NO NUMBER,
EMP_NAME YARCHAR2(150),
MANAGER NUMBER,
SALARY NUMBER
);
guru99_emp_rec emp_det;
BEGIN
guru99_emp_rec.emp_no:= 1001;
guru99_emp_rec.emp_name:=:'XXX';
guru99_emp_rec.manager:= 1000;
guru99_emp_rec.salary:=10000;
dbms_output.put.line('Employee Detail');
dbms_output.put_line ('Employee Number: '||guru99_emp_rec.emp_no);
dbms_output.put_line ('Employee Name: '||guru99_emp_rec.emp_name);
dbms_output.put_line ('Employee Salary: ' ||guru99_emp_rec.salary);
dbms_output.put_line ('Employee Manager Number: '||guru99_emp_rec.manager);
END;
/
Output:
Employee Detail Employee Number: 1001 Employee Name: XXX Employee Salary: 10000 Employee Manager Number: 1000
Code Explanation:
- Code line 2-8: Record type 'emp_det' is declared with columns emp_no, emp_name, salary and manager of data type NUMBER, VARCHAR2, NUMBER, NUMBER.
- Code line 9: guru99_emp_rec variable is declared as 'emp_det' data type. Now this variable can hold the value that contains all the above 4 fields/columns.
- Code line 11: Populating the 'emp_no' field of 'guru99_emp_rec' with value 1001.
- Code line 12: Populating the 'emp_name' field of 'guru99_emp_rec' with value XXX.
- Code line 13: Populating the 'manager' field of 'guru99_emp_rec' with value 1000.
- Code line 14: Populating the 'salary' field of 'guru99_emp_rec' with value 10000.
- Code line 15-19: Displaying the value of the 'guru99_emp_rec' in output.
Example 3: Record Type at Subprogram level-Row level access
In this example, we are going to see how to create a record type at subprogram level and how to populate it as a row level. We are going to create 'emp_det' record_type at subprogram level, and we are going to use the same to populate and to display data from it.
DECLARE TYPE emp_det IS RECORD ( EMP_NO NUMBER, EMP_NAME YARCHAR2( 150), MANAGER NUMBER, SALARY NUMBER ); guru99_emp_rec emp_det; BEGIN INSERT INTO emp (emp_no, emp_name, salary, manager) VALUES (1002,'YYY',15000,1000); COMMIT; SELECT emp_no, emp_name, salary, manager INTO guru99_emp_rec FROM emp WHERE emp_no=1002; dbms_output.put_line (‘Employee Detail’); dbms_output.put_line (‘Employee Number: '||guru99_emp_rec.emp_no); dbms_output.put_line (‘Employee Name: '||guru99_emp_rec.emp_name); dbms_output.put_line (‘Employee Salary: '||guru99_emp_rec. salary); dbms_output.put_line (‘Employee Manager Number: '||guru99_emp_rec.manager); END; /
Code Explanation:
- Code line 2-8: Record type 'emp_det' is declared with columns emp_no, emp_name, salary and manager of data type NUMBER, VARCHAR2, NUMBER, NUMBER.
- Code line 9: guru99_emp_rec variable is declared as 'emp_det' data type. Now this variable can hold the value that contains all the above 4 fields/columns.
- Code line 11: Populating the table emp with data 1002 as emp_no, YYY as emp_name, 15000 as salary and 1000 as manager number.
- Code line 12: Committing the above insert transaction.
- Code line 13: Populating the 'guru99_emp_rec' variable as a row level data from the select query for employee number 1002.
- Code line 15-19: Displaying the value of the 'guru99_emp_rec' in output.
Output:
Employee Detail Employee Number: 1002 Employee Name: YYY Employee Salary: 1000 Employee Manager Number: 15000



No comments:
Post a Comment